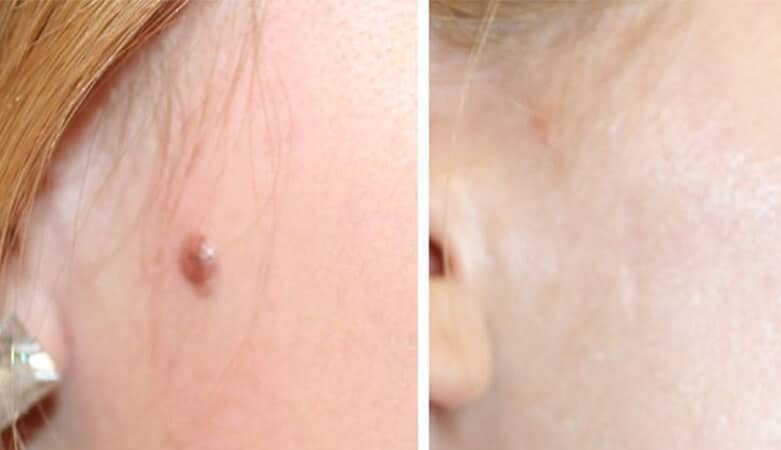
Moles appear in different shapes, colors and sizes on the face and body due to the proliferation and excessive activity of pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) and non-pigmentation cells (keratinocytes).
Moles are divided into congenital and acquired. Acquired moles are usually harmless and appear gradually at older ages. As long as there is no diagnostic evidence and documentation that the acquired mole is malignant, there is no obligation to remove it.
But birthmarks, especially moles with a diameter of more than 20 cm, are prone to malignancy.
These types of moles should be surgically removed as soon as the general condition of the baby at birth allows, but in the case of small congenital moles, there is less chance of malignancy and if the size or shape of these moles does not change, They can be passed without any special treatment.
Moles are caused by various reasons such as genetic history, natural hormonal changes during growing age, pregnancy, use of immunosuppressive drugs (chemotherapy or light therapy), history of hormonal disorders (hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism or internal metabolic diseases), contact with Caustic and chemical substances and long-term exposure to sunlight are created.
But the appearance of a mole will have an adverse effect on the beauty of your skin.
Today, there are different methods for tattooing that will help you maintain your beauty.
In the following, there are different methods available to remove moles. In removing a mole, a specialist doctor must first perform a detailed examination to identify the type of mole, and if there are no significant side effects, he is allowed to remove the mole.
Because among the moles, some are among dangerous moles and it is not recommended to remove them, and the diagnosis of this case is the responsibility of a specialist doctor.
There are various methods such as laser, surgery, exfoliation, microdermabrasion to remove and reduce moles, which is chosen according to the depth and type of mole and other cases. The diagnosis of the type of treatment method is the responsibility of the specialist doctor.
What moles can be removed?
In general, any mole that has one or more unusual appearance, such as the asymmetry of the lesion, the irregularity of the border, and the uniform color of the mole, or if its size is more than seven millimeters, should be removed.
Moles that continue to grow in old age or become dark and change in shape should also be removed.
Previously, some doctors recommended that moles that are subject to constant friction or irritation (such as moles in the beard area of men or in the belt or elbow area) should be removed because they have the possibility of becoming malignant, but today there is no such belief.
Of course, some moles are unsightly and unpleasant, and the patient goes for facial mole surgery in terms of beauty or because of the insistence of others, and mole removal in these cases must be done carefully and following the principles of surgery to avoid or minimize the risk of a surgical site.
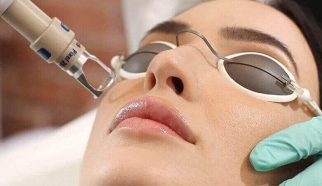
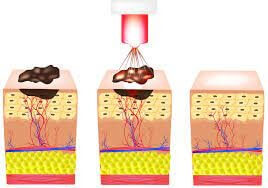
Laser treatment
Most of the world’s scientific societies do not approve the removal of moles with laser because the effect of laser radiation on the pigment-producing cells of the mole in the long term is still not completely clear.
Also, the big drawback of this method is that there is no sample left to send to the pathology laboratory, if as a rule, any tissue from the body, especially the mole, that is removed, must be sent to the laboratory for pathology.
Laser treatment is done in one or more sessions according to the type of mole, its depth and extent. If the mole is deep, surgical methods are preferred over laser.
surgery
The best way to remove a mole is surgery. In the laser method, only the active color of the mole is destroyed, and the mole cells are still left. But the probability of returning the blank that is removed with a razor is very low.
If the vulva is full of color and hairy, surgical procedures are usually recommended. But if the size of the mole is millimeter and flat, the laser method is used instead of surgery. For example, it is not recommended to remove a mole on the neck or chest, because the risk of excess flesh in these areas is very high.
If the mole recurs after removal, you must see a doctor. The possibility of scarring (remaining a scar) after mole surgery depends on the skill of the doctor and the type of skin repair of the patient.
Some people are prone to the formation of extra skin at the surgical site, and in some parts of the body, the risk of forming a boil at the surgical site is higher.